Systematic Land Inventorization: Comparison Of Systems
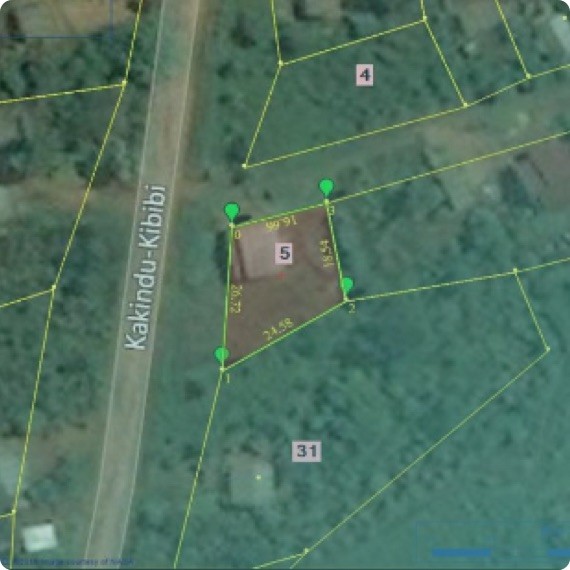
The inventory system for land is a hierarchical system that consists of seven levels. The first three levels contain data related to the climate and geology of land, divided into provinces, sections, and sub-sections. The bottom four levels involve data concerning land type as well as its association, phase, and site. Within these categories exist various classes defined by details about landforms, soils, and climax plant types. Every level in systematic land inventorization offers information related to land resources that is suitable for particular planning requirements. Further subdivisions can be made in the abovementioned classes so that more exact information can be gained at a lower level of The classes in each level can be subdivided to provide more specific data at one or more of the lower levels. The data can also be consolidated for generalized information at a larger level. Discussing the Various Kinds of Systematic Land Inventorization Land system inventor...




